LLM2LLM
LLM2LLM: Boosting LLMs with Novel Iterative Data Enhancement
Introduction
The core issue addressed in this paper is the challenge of improving reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) with limited training data. Under such data scarcity, fine-tuning, while effective for adapting models to specific tasks, may not adequately address the challenge of increasing LLM reasoning capabilities. The LLM2LLM approach introduces a novel solution that focuses on generating targeted, challenging data points to directly improve reasoning abilities.
Research Gap
The paper targets the challenge of enhancing reasoning capabilities of LLMs in situations where available training data is scarce. Distinguishing from other data augmentation techniques, this research focuses on selectively augmenting only those data points which the LLM initially fails to predict correctly, rather than all data points. This method aims at efficient improvement, concentrating efforts on revising only the model’s weaknesses rather than expanding the whole training dataset.
Solution
LLM2LLM
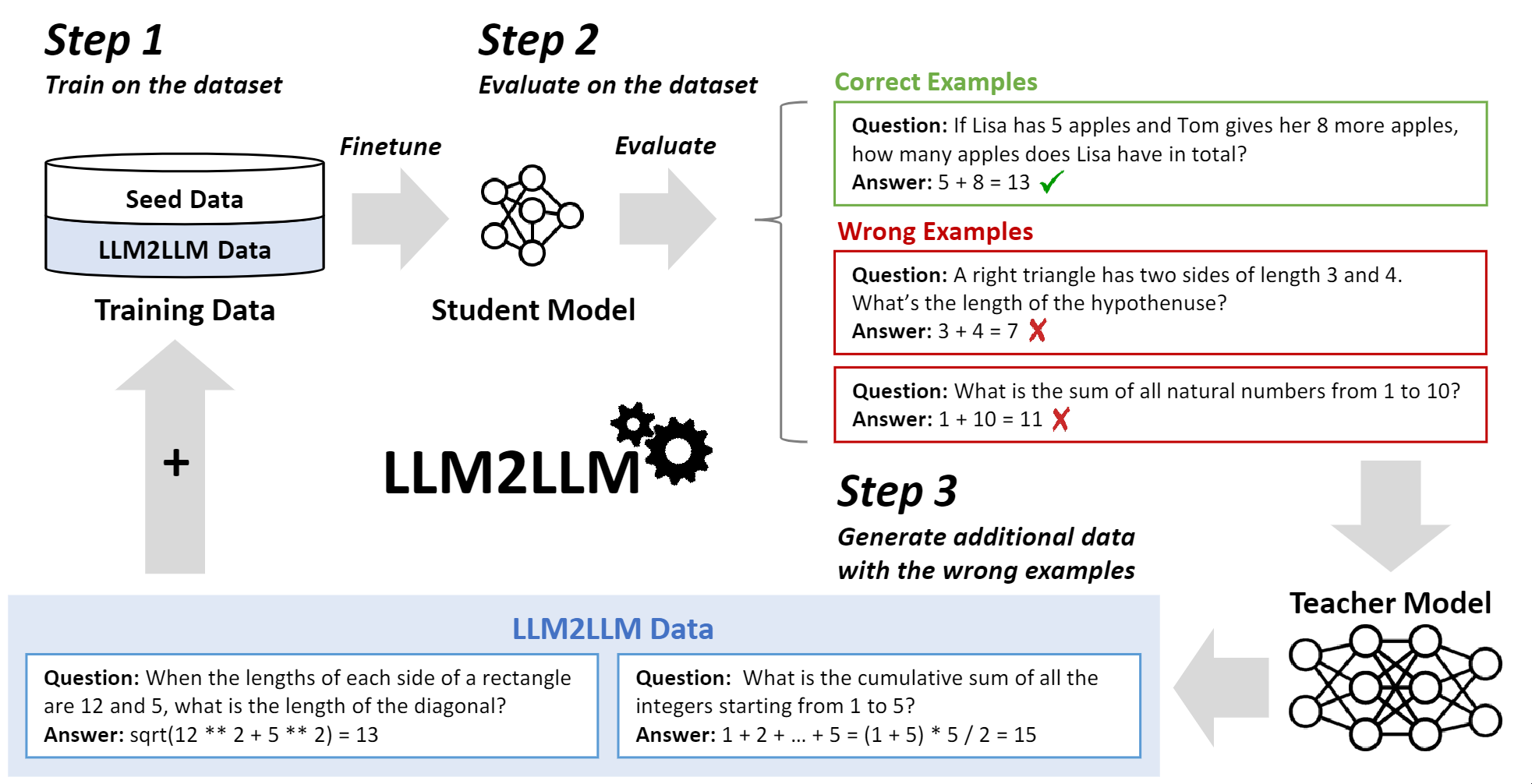
The solution proposed in this paper is called LLM2LLM, the steps of which are as follows:
- First, an LLM with a good enough reasoning ability is chosen as the teacher model to follow the instructions for data augmentation. It does not necessarily need to be bigger than the student model.
- Second, the seed dataset is fed as input to the student model. The performance of the model is measured and the data points for which the prediction of the model was incorrect are filtered.
- Third, these filtered data points are fed to the teacher model for being augmented. The augmented data should be directly produced from the seed data points. In other words, they never use the augmented data points to generate another set of augmented data.
- The two datasets (seed and augmented) are passed to the student model for another iteration of evaluation.
- This process can be repeated \(n\) times, depending on the target level of accuracy.
They have used LLaMa2 for the student model and GPT3.5, GPT4-Turbo, and LLaMa2 for the teacher model. An overview of LLM2LLM is depicted in the following figure:
Knowledge Distillation and Data Augmentation
Knowledge distillation and data augmentation both use teacher and student models but serve different purposes. In knowledge distillation, the teacher model’s knowledge is transferred to the smaller student model, aiming to retain performance while reducing model size. However, data augmentation focuses on enriching the training data—often through the teacher model generating new examples—to improve the student model’s learning and generalization. The key difference lies in their objectives: distillation seeks to compress and transfer knowledge, while augmentation aims to expand the training dataset for better model robustness.
Comment: The paper (the last paragraph on the first page) mentions fine-tuning LLMs as a solution for handling very long contexts. However, this perspective may overlook the inherent limitations of fine-tuning in expanding the model’s capacity to directly manage longer sequences. While fine-tuning optimizes a model’s performance on specific tasks, it does not directly increase the model’s ability to process or comprehend longer contexts.
Experiments
The primary aspects of the experimental setups are as follows:
- Tasks: Mathematical reasoning, question answering, sentiment analysis, and text comprehension
- Dataset: GSM8K, CaseHOLD, SNIPS, TREC, SST-2
- Baselines: Fine-tunned LLaMa2, AugGPT, EDA
- Evaluation Metrics: Accuracy (%)
Conclusion
This paper proposes a method to enhance the performance of LLMs in scenarios with limited training data. It introduces an iterative data augmentation strategy using a “teacher” LLM to generate synthetic data based on incorrect predictions by a “student” LLM. This process aims to improve the student model’s performance by only focusing on challenging examples. The results show significant improvements in various datasets, highlighting the method’s potential to reduce the need for extensive data augmentation and improve LLMs’ effectiveness in data-constrained tasks.