GenRec
GenRec: Large Language Model for Generative Recommendation
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of recommendation systems, the integration of large language models (LLMs) has emerged as a groundbreaking approach with significant potential. This paper introduces a model, GenRec, which leverages the power of LLMs for generative recommendation tasks. By directly generating target items based on comprehensive textual data understanding, GenRec demonstrates the potential of LLMs in revolutionizing the recommendation landscape.
Research Gap
The paper introduces the concept of generative recommendation, wherein the target item is directly generated, in contrast to traditional discriminative recommendation systems that calculate ranking scores for each candidate item. Therefore, they proposed GenRec model, which operates as an LLM-based system that leverages textual user interaction data to provide personalized item recommendations.
Personal Opinion: However, a notable limitation of the paper is the lack of comprehensive comparison with other existing LLM-based recommendation systems. While it compares GenRec with P5, which primarily operates based on user and item IDs, the paper falls short in providing a thorough analysis and comparison with other state-of-the-art LLM-based recommendation models that incorporate textual information. Also, since its focus is on generative recommendation task, it was better to mention the hallucination problem as well.
Solution: GenRec
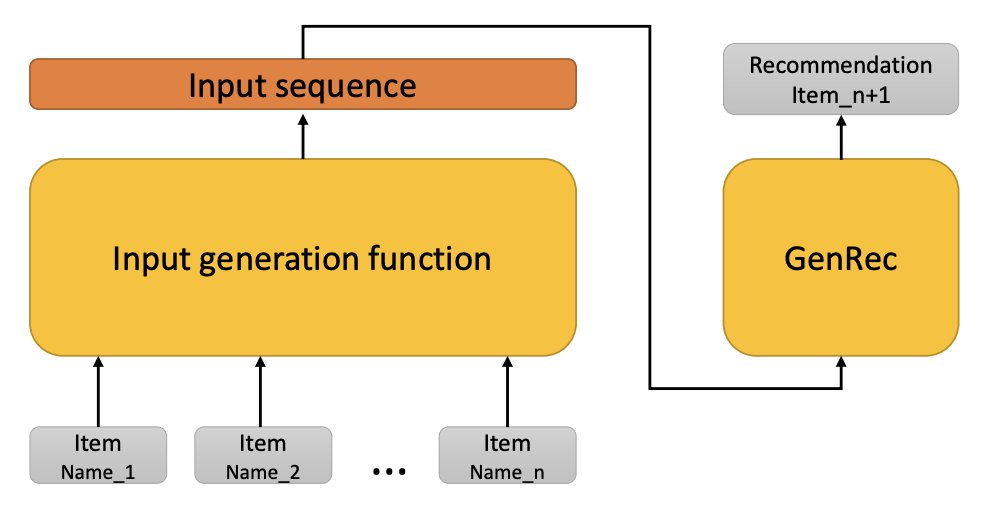
GenRec primarily leverages an LLM to generate the next recommended item based on a formatted prompt. This prompt consists of three parts:
-
Instruction: A fixed template for each recommendation task that provides specific guidance to the LLM regarding the nature and context of the recommendation task.
-
Input: Concatenation of the names of the items with which the user has previously interacted. This historical interaction data serves to provide context to the LLM, allowing it to understand the user’s preferences and behavior.
-
Output: A segment left for the LLM to complete, representing the predicted next item for the user to interact with. The LLM’s understanding of the user’s preferences and historical interactions enables it to generate informed recommendations for the user.
While the GenRec model utilizes the LLaMA large language model as its backbone, it is not limited to any specific LLM. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of the GenRec approach to various LLMs, depending on the specific requirements and context of the recommendation task at hand.
Here is a brief overview of the architecture of GenRec:
This is an example of the formatted prompt in GenRec:

Experiments
The experiments conducted in the paper aimed to evaluate the performance of the proposed recommendation system, GenRec, in sequential recommendation. The primary aspects of the experimental setup are outlined below:
- Datasets: The experiments were performed on two real-world datasets - the Amazon Toys dataset and the MovieLens-25M dataset.
- Baseline Methods: The paper compared the performance of the GenRec model with the P5 model, which operates based on user and item IDs.
- Evaluation Metrics: The evaluation metrics utilized are Hit Ratio (HR), Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG). Also, the core LLM used in GenRec is LLaMA.
- Results: While P5 showed better performance on the Amazon Toys dataset, the GenRec model exhibited significantly improved results on the MovieLens 25M dataset.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the GenRec model presents an LLM-based recommendation system. By effectively leveraging the rich contextual information embedded within LLMs, GenRec provides a reasonably accurate and personalized recommendations.