Paper Review - Week 34
Here is the list of the most interesting papers published in this week:
LLMRec: Benchmarking Large Language Models on Recommendation Task
Introduction
Despite the developments in LLMs, the integration of LLMs into the domain of recommendation systems has not been thoroughly explored. This research aims to bridge this gap by proposing LLMRec, an LLM-based recommender system crafted for benchmarking LLMs across various recommendation tasks.
Solution: LLMRec
The key steps involved in the LLMRec system are:
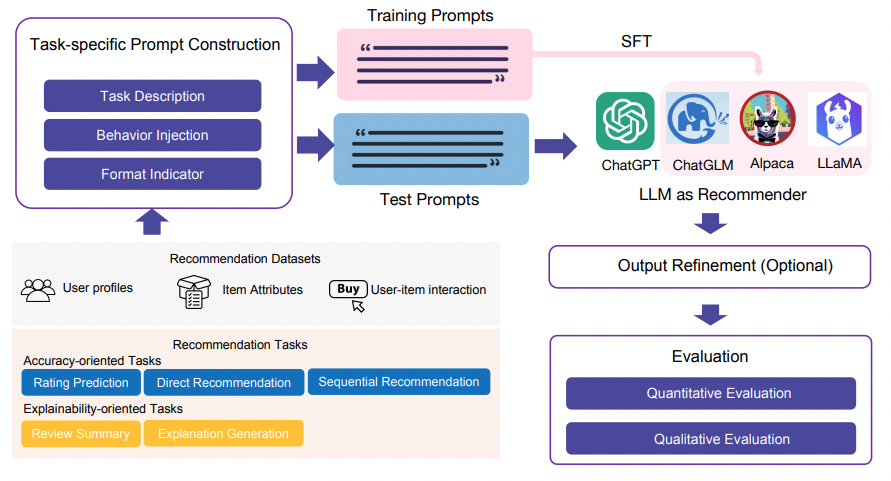
- Prompt Generation: Creating task-specific prompts using modules like task description, behavior injection, and format indicator modules. It seems to utilize template-based prompts for the different recommendation tasks, and it doesn’t explicitly mention an approach for optimizing the prompts themselves.
- Model Processing: Passing the created prompts to the LLMs, with the option of fine-tuning the models when necessary.
- Output Refinement: Evaluating the results using the output refinement module, which checks and refines the output of the LLMs, particularly addressing any issues related to hallucination or non-compliance with the desired output format. It doesn’t explicitly mention specific guidelines for the output refinement module. However, the concept of the output refinement module implies the need for a mechanism that can check and correct the output of the LLMs, particularly when it comes to hallucinations or outputs that do not meet the desired format or quality.
- Evaluation: Comparing the performance of the LLMs with various benchmarks and baseline methods for different recommendation tasks, including rating prediction, sequential recommendation, direct recommendation, explanation generation, and review summarization.
An overview of the architecture of LLMRec is depicted in the following figure:
Experiments
The primary aspects of the experimental setup are outlined below:
- Benchmarks: The benchmarks include various recommendation tasks, such as rating prediction, sequential recommendation, direct recommendation, explanation generation, and review summarization. The system evaluates the performance of off-the-shelf LLMs, including ChatGPT, ChatGLM, LLaMA, and Alpaca, and compares their results with state-of-the-art methods and baseline models for each specific recommendation task.
- Datasets: The study primarily focuses on evaluating the Beauty category within the Amazon dataset, which comprises customer review text and associated metadata for products.
- Evaluation Metric: For rating prediction, the evaluation metrics used are Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE). For sequential and direct recommendation tasks, the evaluation metrics include HR and NDCG. For explanation generation and review summarization, the evaluation metrics involve BLEU and ROUGE.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study has shed light on the potential of LLMs in the field of recommendation systems. Through the development and evaluation of the LLMRec system, they have demonstrated that LLMs, while exhibiting limited proficiency in certain accuracy-based tasks, showcase significant promise in explainability-based tasks.
Here are some more articles relevant to this one: